Research
1. Wireless Body Area Communication
With the rapid progress of small electronic devices and wireless communication technology, wireless body area networks (WBAN) have drawn considerable attention in medical services and healthcare applications. WBANs are divided into wearable BAN and implant BAN. Wearable BAN is based on on-body communication which aims to monitor a person's healthy situation in daily life, whereas implant BAN is based on in-body communication which aims to transmit medical data or image from the inside to outside of human body such as capsule endoscopes. Possible frequency bands for WBAN include 10-50 MHz human body communication (HBC) band, 400 MHz band, 2.4 GHz band and UWB.
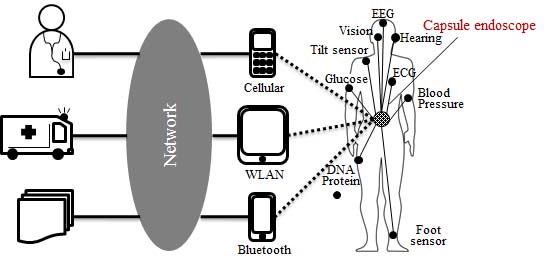
In our laboratory, we are focusing on HBC band, 400 MHz band and UWB to tackle the following research topics:
- On-body / in-body channel modeling
- On-body / in-body modulation and de-modulation schemes
- Localization and tracking of in-body communication device for capsule endoscope
- Development of various body area transceivers and their feasibility measurement
- Real-Time Transmission of Vital Signals by Human Body Communication Technology
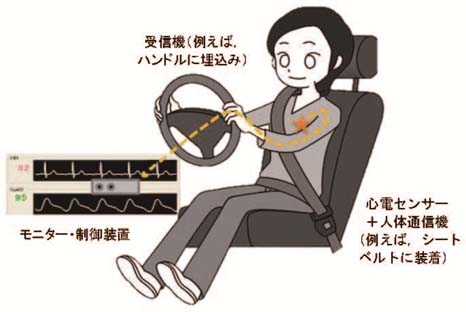
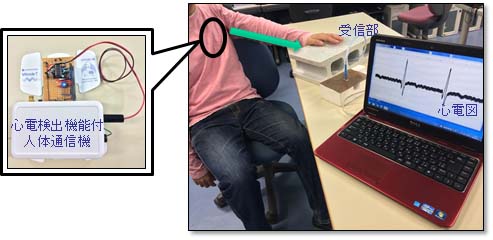
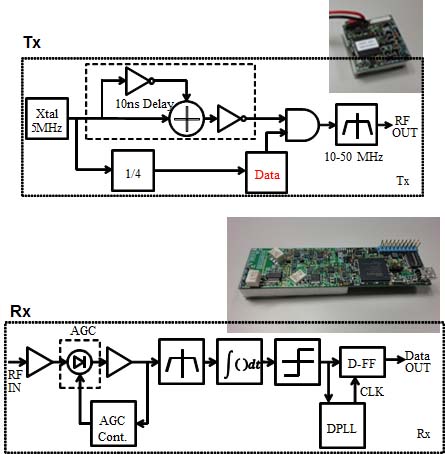
One of promising applications is to monitor driver's health conditions for assisting automatic drive. In this scenario, some vital sensors are placed on the driver's body to collect healthcare data such as electrocardiogram (ECG), blood pressure and pulse rate. The vital sensors may be embedded in the driver's seat, seat belt, or steering wheel to make the driver unconsciously wear these sensors. A HBC transceiver is used to send these data to a control unit for analyzing the driver's health condition and generate warning signs or make automatic control of car, if necessary, for safety driving. As an element technology, we have developed an impulse radio (IR) type HBC transceiver for ECG signal real-time transmission:
 |
 |
【Topic 2】
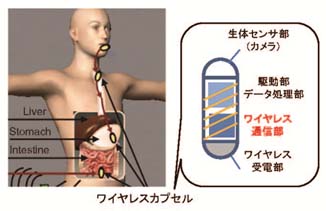
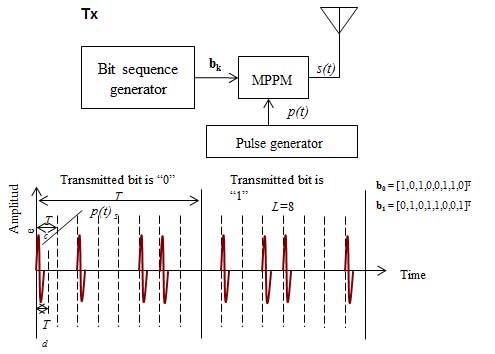
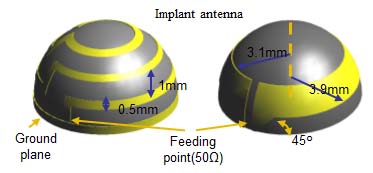
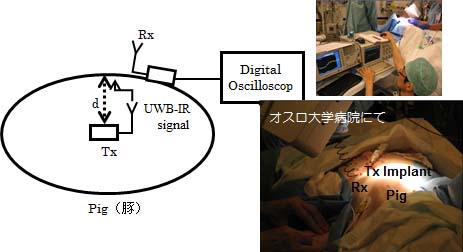
- Development of High-Speed Wideband IR Transceiver for Capsule Endoscope Application
We have developed two in-body transceivers in the UWB low-band and the HBC band, respectively, for real-time image/video transmission of wireless capsule endoscope. The transceivers employ a wideband impulse radio (IR) technology with multiple pulse position modulation (MPPM) scheme. From a living animal experiment under the support of medical doctors in a hospital, our developed transceivers have demonstrated a bit error rate of 10-2 at an in-body depth of at least 12 cm at a data rate as high as 1 Mbps.
 |
 |
 |
 |
【Topic 3】
- Wirelessization of control signal transmission to myoelectric hand
We developed a wireless technique for sending the control signal to a myoelectric artificial hand based on human body communication (HBC). First, a detection circuit detects the myoelectric signals by using three electrodes attached to the arm. Then the detected myoelectric signals are transmitted to a myoelectric hand control unit by a HBC-based transceiver. The myoelectric hand are thus controlled and operated based on the received myoelectric signals.
Technical features:
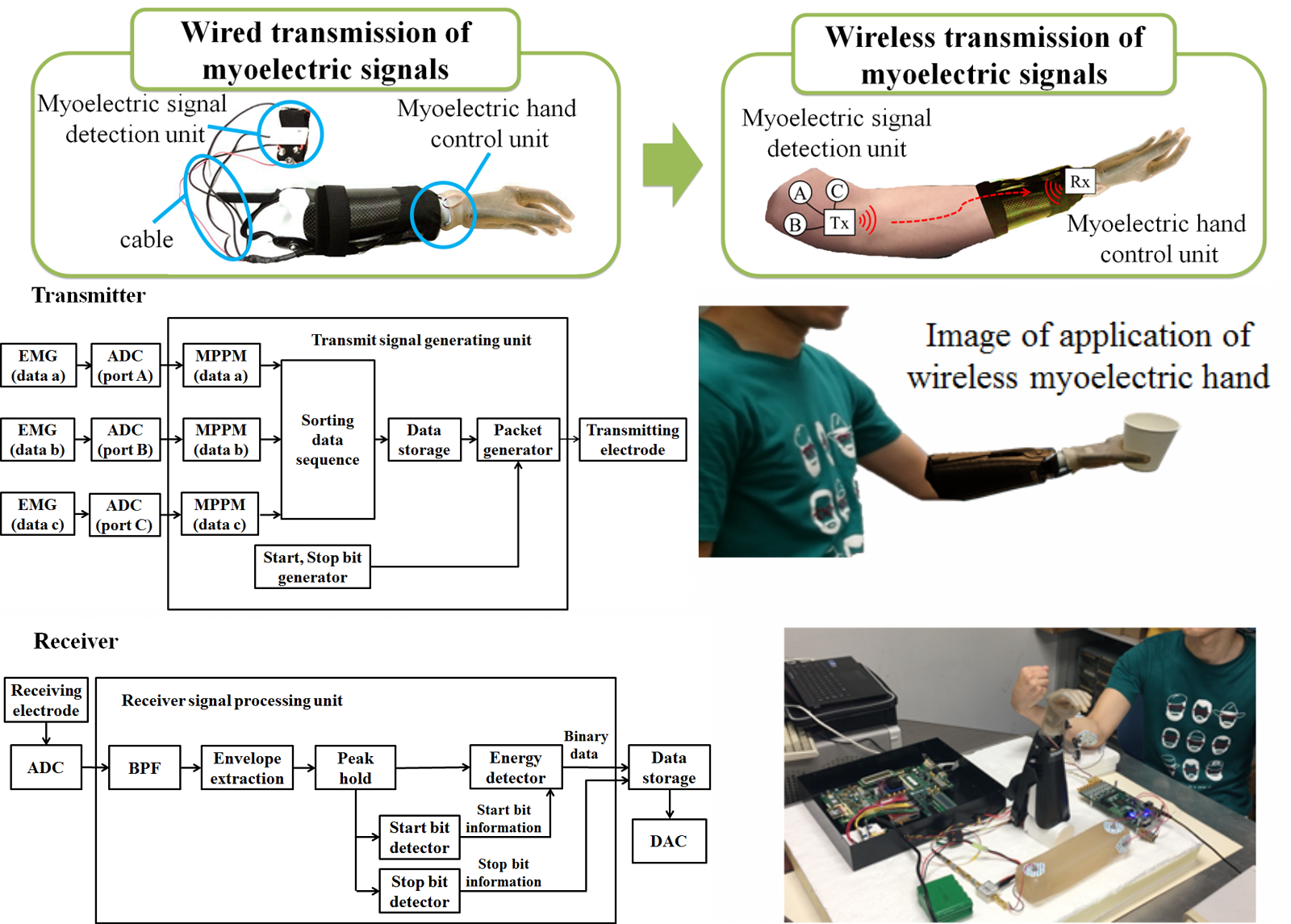 |
【Topic 4】
- Localization/Tracking Methods for Capsule Endoscope
It is important to estimate the location of implant communication devices, i.e., wireless capsule endoscope, because no one knows the location in advance due to its movement inside a human body. Therefore, we have developed location tracking methods with radio frequency signals transmitted from the capsule endoscope.
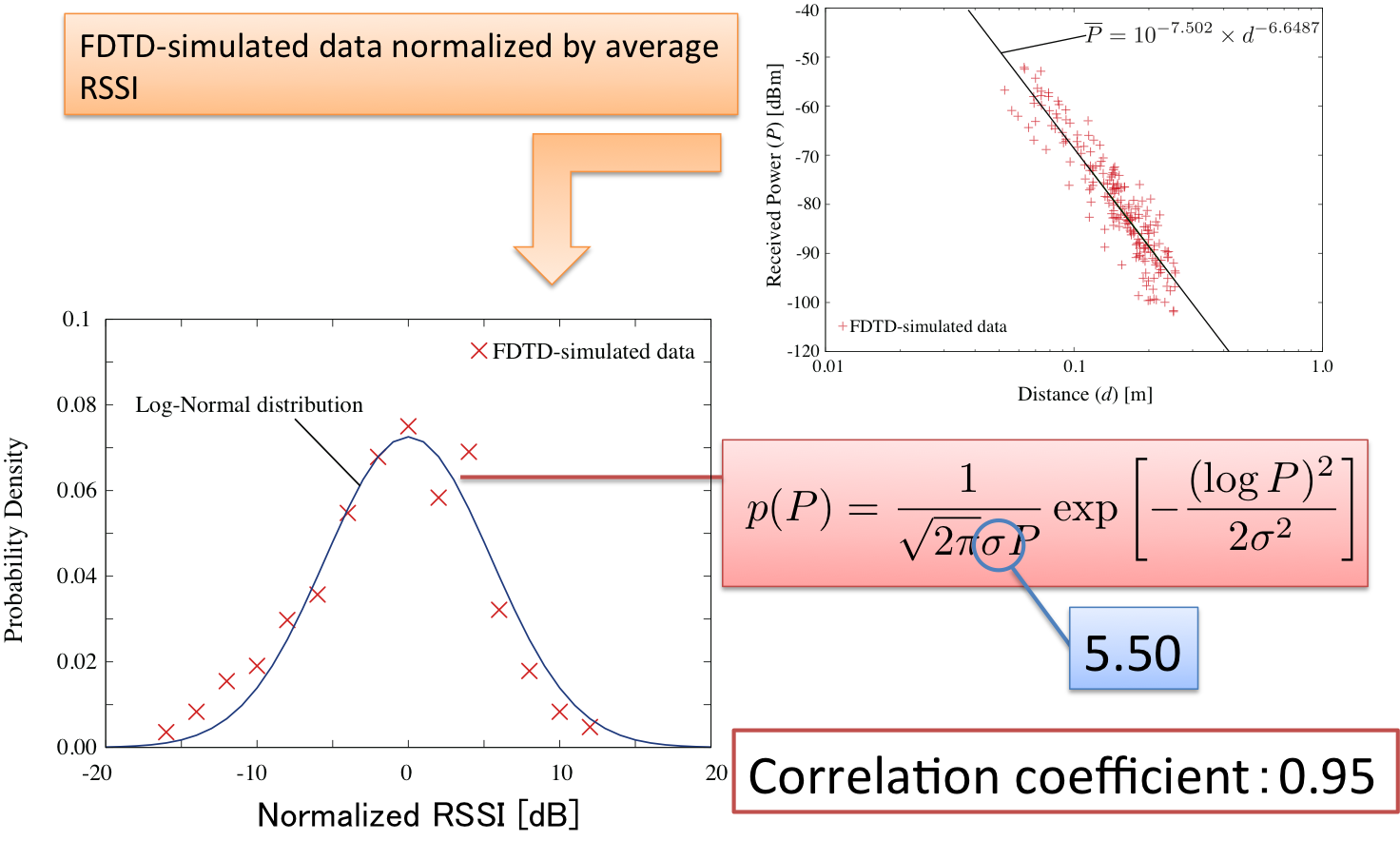
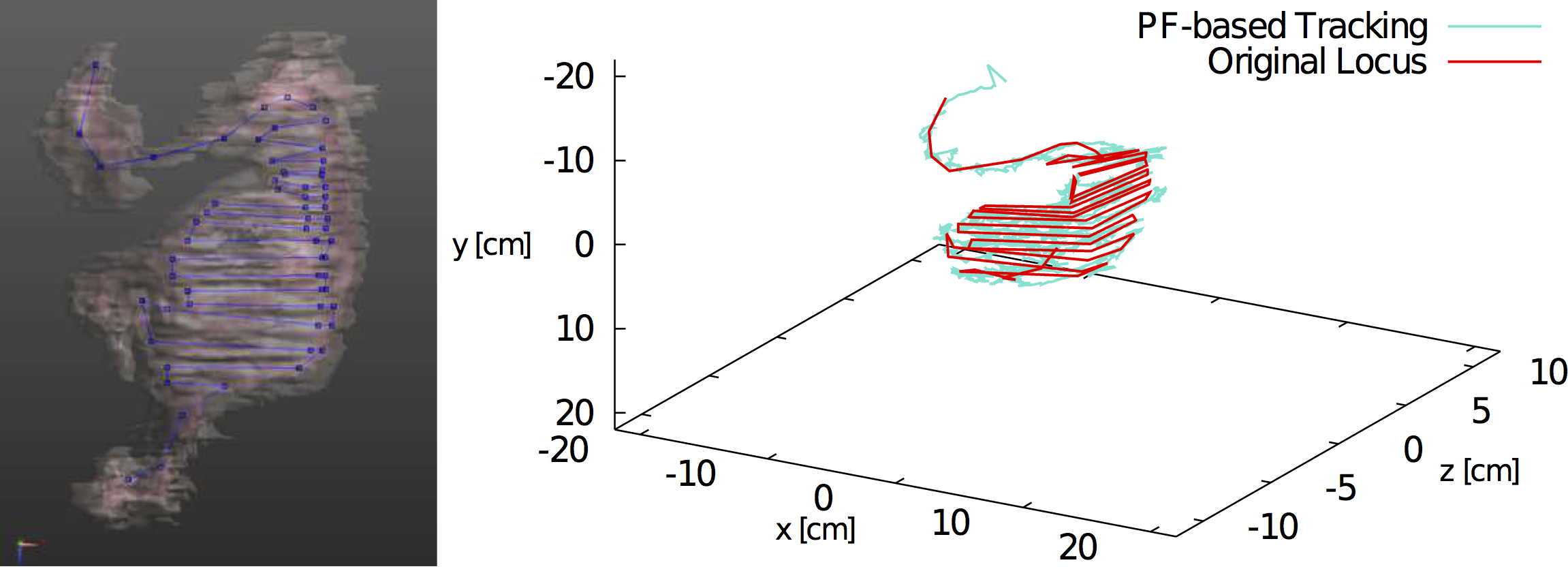
2. Biomedical EMC
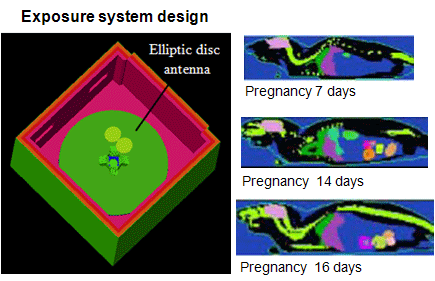
For realizing a body area communication system, it is essential to secure its safety to human body and reliability in use. There is an increasing public concern for possible biological effect of electromagnetic waves as well as potential electromagnetic interference problems for implant medical devices such as cardiac pacemaker. In our laboratory we are tackling
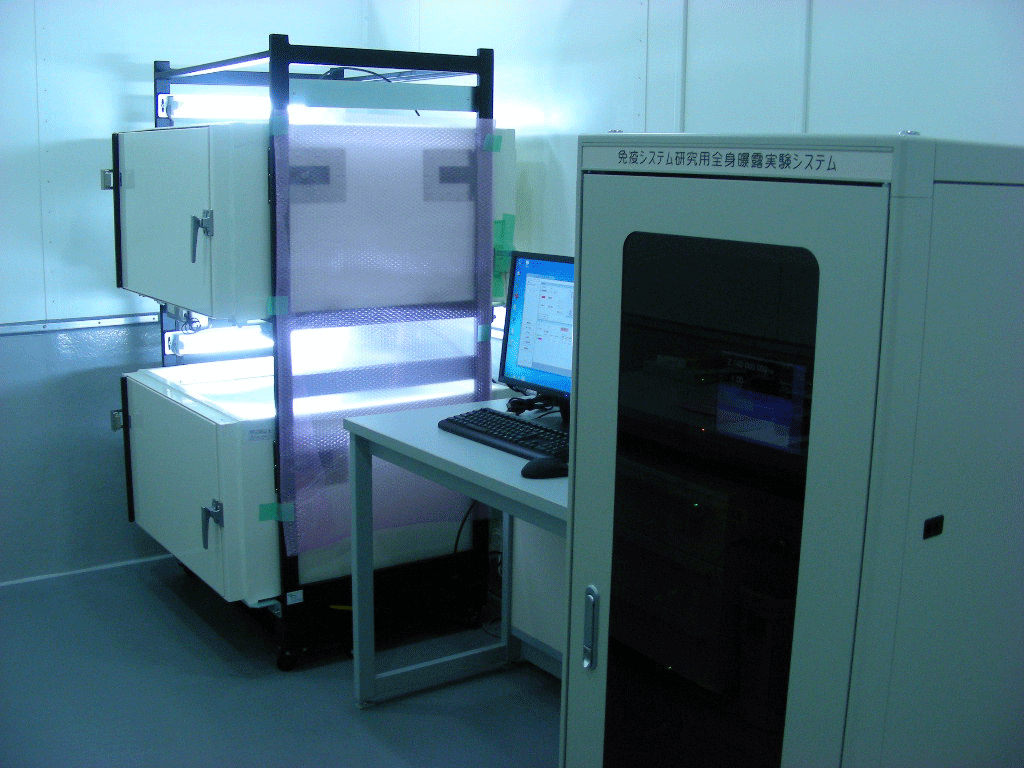
- to develop various exposure systems of animal experiment for bio-effect testing
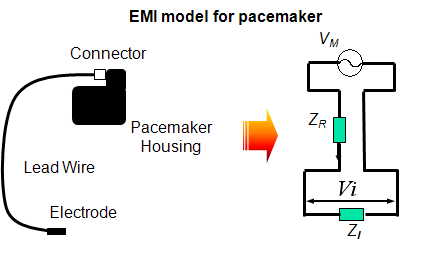
- to clarify mechanism and quantify level of electromagnetic interference for cardiac ?pacemaker
from both electromagnetic field and electric circuit approaches.
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
|